Dealing with eczema on the face, a persistent skin condition marked by redness, inflammation, and itching, poses unique challenges. The discomfort and visibility of facial eczema prompt many to seek effective treatments to alleviate symptoms and enhance their well-being. This article explores various approaches and methods for treating eczema specifically on the face.
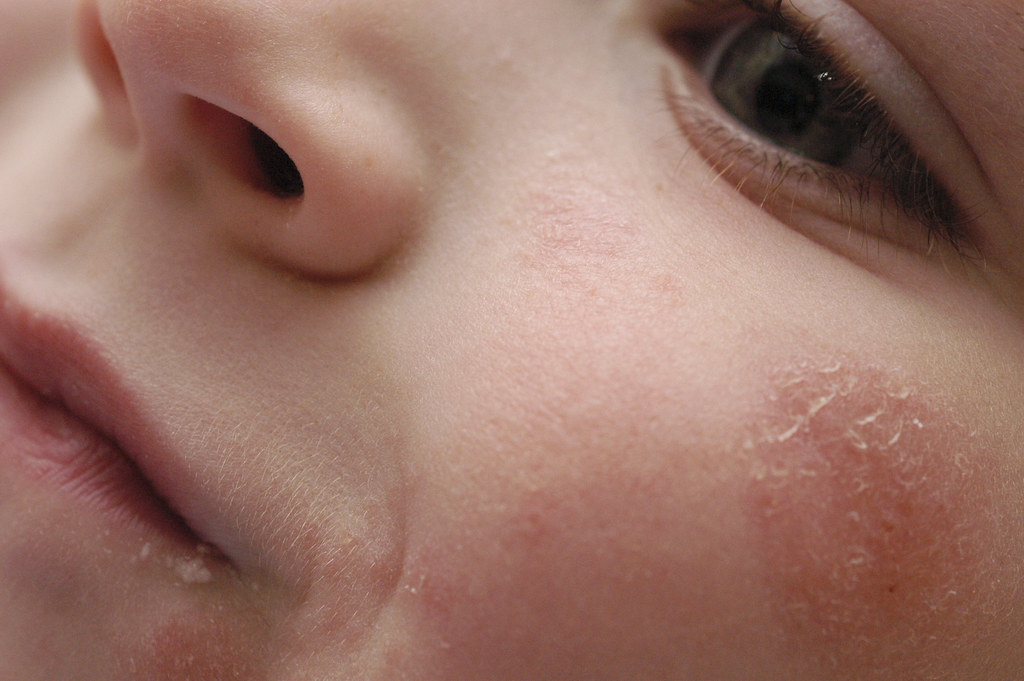

Understanding Facial Eczema:
Facial eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, commonly affects the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead. Given the sensitivity of facial skin, adopting a targeted treatment strategy is crucial.
- Gentle Skincare Routine:
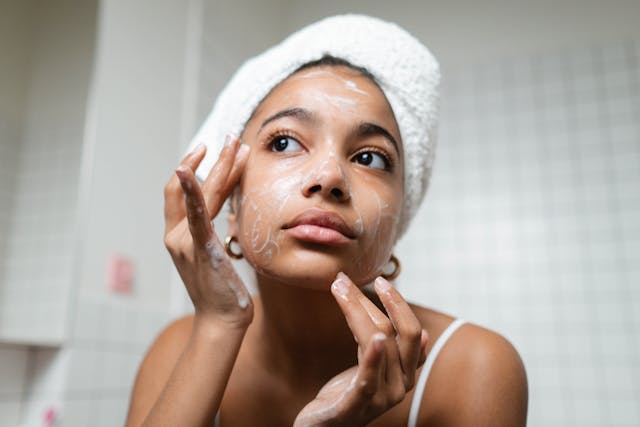

- Utilize mild, fragrance-free cleansers for facial cleansing.
- Steer clear of hot water to prevent the skin from losing its natural oils.
- Gently pat the face dry to minimize irritation.
- Choose hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic moisturizers to keep the skin adequately hydrated.
- Topical Steroids:
- Healthcare professionals often prescribe topical steroids to alleviate inflammation and itching.
- It is imperative to adhere to the prescribed use of steroids, as prolonged usage may lead to skin thinning.
- Mild steroids are generally recommended for facial application to reduce potential side effects.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
- Non-steroidal creams like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus effectively manage facial eczema.
- They function by regulating the immune response and reducing inflammation without the drawbacks associated with prolonged steroid use.
- Moisturization:
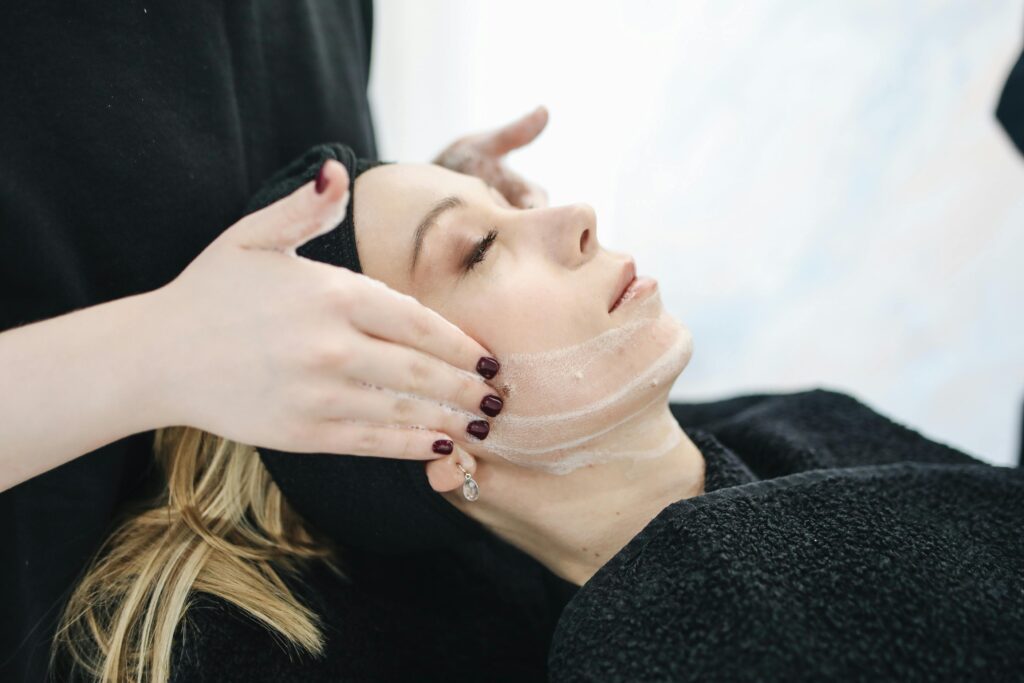
- Regular, thorough moisturization is crucial for maintaining the skin’s barrier function.
- Opt for moisturizers containing ceramides, aiding in the repair of the skin barrier.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing to retain moisture.
- Identifying Triggers:
- Maintain a journal to pinpoint potential triggers that worsen facial eczema, such as specific skincare products, allergens, or environmental factors.
- Once identified, take measures to minimize or avoid exposure to these triggers.
- Prescription Medications:
- In severe cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe oral medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.
- Such medications are typically reserved for cases unresponsive to topical treatments.
- Phototherapy:
- Under professional supervision, UV light therapy can be beneficial for certain individuals with facial eczema.
- Phototherapy aids in reducing inflammation and itchiness.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, as stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Sunscreen use and limiting sun exposure help prevent further irritation.
Conclusion:
Effectively managing facial eczema requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing proper skincare, targeted topical treatments, identification of triggers, and, in severe cases, prescription medications. Consulting with a dermatologist is essential to formulate a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs. With proper care, individuals can significantly improve facial eczema symptoms and promote overall skin health.
Fantastic beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your site, how could i subscribe for
a blog site? The account helped me a acceptable deal.
I have been tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast provided vibrant clear concept